SaaS (Software as a Service) is a hugely popular delivery model used by businesses around the world. For several years, SaaS has been used to deliver applications (as a service) over the Internet. In this article, we will provide you with a brief overview of this wonderful concept.
Definition
SaaS has a simple underlying concept. It is a software delivery model that allows businesses to access applications over the Internet. A SaaS-based application functions as a web-based service that allows employees of an organization to access tasks and data online in an organized manner.
Origin
This concept's origins can be traced back to the computing revolution of the 1960s. This decade witnessed several mainframe providers (such as IBM) offering computing services on a time-sharing basis. These providers offered database and virtual storage services to big-scaled organizations.
The 1990s saw the rise of Application Service Providers (ASPs). ASPs revolutionized centralized computing by taking it a whole new level. ASPs provided solutions that hosted and managed business applications. Companies that signed up for such services didn't have to worry about the technology environment within their organization because it was outsourced to ASPs. This allowed companies to focus on their core business areas.
SaaS is an extension of ASP. The acronym SaaS first appeared in a February 2001 article published by the Software & Information Industry Association.
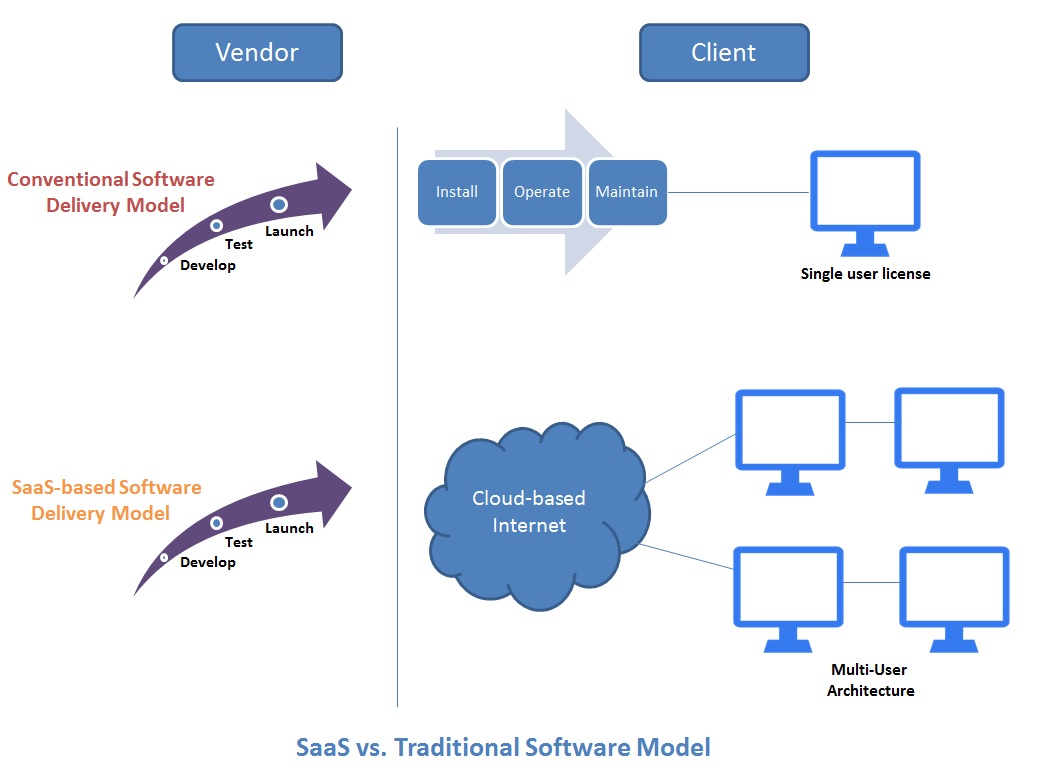
Working
As shown in the figure above, SaaS-based software delivery models offer a radical and positive departure from how software applications were delivered earlier by vendors. Traditional software delivery models relied on selling software to clients on purchase of a license. The client would then have to install and deploy the software at his office. Further software updates and license renewals were then done by collaborating with the vendor.
A couple of years ago, vendors began relying on the Internet to deliver software. The ASPs mentioned above allowed clients to download software from the Internet for a fee. After download, installation and maintenance practices were similar to those followed in traditional delivery models.
SaaS takes software delivery to a new level by serving as an end-to-end hosted solution. Employees working on such a model can log in to the Internet and work from anywhere in the world. There is no need to download any software to the local machine.
Benefits
1. Less pressure on the company's internal IT infrastructure: SaaS-based solutions are provided by 3rd-party vendors. A business won't have to invest heavily in creating an internal IT infrastructure to augment their technology needs. All technology functions can be accessed online by logging into the Internet.
2. Cost-efficiency with a lot of savings: Businesses stand to gain a lot since there is no need to install and maintain software or specialized IT equipment. SaaS delivery models are significantly cheaper than traditional models to start with.
3. No licensing hassles: Traditional software models required businesses to purchase licenses based on the number of users. No such hassles with SaaS. A simple tweak in the SaaS agreement will allow more users to access the network.
4. Convenient hardware and software updates: Since the vendor is in charge of maintaining IT infrastructure, you won’t have to worry about making frequent hardware and software updates. The vendor takes care of everything.
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) and Platform as a Service (PaaS)
Here are two concepts that work with SaaS to make cloud computing a success.
PaaS is a cloud-based computing platform that works entirely to create software over the Internet. It differs from SaaS in its concept because it doesn't just deliver applications but builds them as well.
IaaS delivers infrastructure on an on-demand basis. Servers, networks, operating systems and databases are provided to the client based on their technology requirements.

